Science and Technology Class 09
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:09 PM)
ISSUES AND CHALLENGES WITH NANOTECHNOLOGY (05:13 PM)
- Health and safety concern- Because of the toxicity of nanoparticles
- Misuse of nano-technology- For example- Military applications, use in gene editing for designer babies.
- There are challenges in developing appropriate regulations for nano-materials, nano-devices, and nano-systems.
- There are environmental concerns regarding the unsafe handling of nanomaterials. The long-term effects of nano-materials on ecosystems and bio-diversities are still being investigated.
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (05:29 PM)
- Framework
- 5G- Cloud computing, Edge computing,
- Computing- Supercomputers, Quantum computers, Quantum communication.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
- Internet- Satellite-based internet, Dark web, net neutrality
- AI, Robotics
- Data protection.
COMMUNICATION (05:32 PM)
- Electromagnetic waves
- Waves- It is some sort of disturbance that is traveling in a periodic motion.
-

- Waves always require a medium to propagate. Sound cannot propagate into space. Newton thought that light is a particle.
- Huygen proposed that Light is a wave. Light is traveling through a medium called ether. [* This was rejected after conducting an experiment]
- Maxwell proposed that Light is an electromagnetic wave and this wave does not require any medium to propagate.
-

- Electric fields and magnetic fields are phenomena of Magnetism. Changing the magnetic field produces an electrical field and changes in an electrical field lead to the production of the magnetic field.
- Properties of waves
-
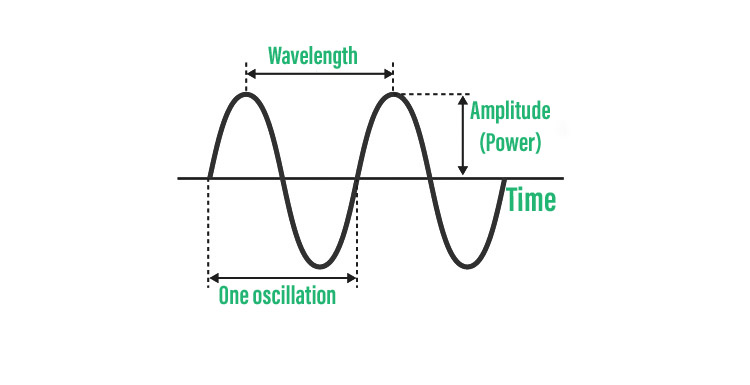
- Frequency= No. of vibrations per section
- Speed= V= λf
- In case of electromagnetic waves it becomes C= λf, C= 3* 10^ 8 m/s
-

- The wavelength of Visible light is 370 Nm to 780 Nm
-
- E∝f
- E= h* f
- h= Planck's constant
LIFI (Light Fidelity) or Visible light communication (06:14 PM)
- In this technology, visible lights using LED bulbs (Ultraviolet and Infrared are also being explored) are used for communication. It is a wireless communication technology to transmit data. It works by modulating the intensity of light emitted by an LED bulb which can be detected by a receiver.
- It can attain very high speed more than 50 times compared to Wifi, however, there are certain challenges such as limited coverage (Confined to a room in which they are generated), interference from the other light sources, and scalability amongst others.
-
 .
.
KEY TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (06:51 PM)
- Signal
- Information converted in electrical form and suitable for transmission is called a signal
- Signal can be of two types- Analog signal and Digital signal
-

- Analog signals are continuous variations of voltage or current. Sound and picture signals on TV or in a typical radio are examples of analog.
- Digital signals- These are those which can take only discreet step-wise values of 0 and 1. This is called a Binary system. Currently, there are many coding mechanisms used to represent letters, numbers, and pixels in binary systems. For example- the most accepted coding mechanism is the ASCII system (American standard code for information interchange).
- Noise
- It refers to unwanted signals that tend to disturb the transmission and processing of the message signals.
- The loss of strength of a signal while propagating through a medium is called attenuation.
- Amplification is the process of increasing the amplitude and consequently the strength of a signal.
- Range
- It is the largest distance between a source and a destination up to which a signal is received with enough strength.
- Bandwidth
- It refers to the frequency range over which equipment operates or the portion of spectrum occupied by the signal i.e. different types of signal require different bandwidths.
- The transmission medium also provides different bandwidths. For example- Older cables often made of copper provide less bandwidth, in comparison Air provides more bandwidth.
- The highest bandwidth is provided by optical fibre cables.
- Optical fibre cables provide high bandwidth because the Signal undergoes total internal reflection and signal strength does not deteriorate despite transmission over 1000s of KM.
MODULATION (07:45 PM)
- The original low-frequency signal can not be transmitted to long distances therefore at the transmitter, the information contained in the low-frequency signal is superimposed on a high-frequency wave which acts as a carrier of the information. This process is known as modulation.
- At the receiver, information from the modulated signals has to be retrieved which is called de-modulation.
-

- Modulation is of three types
- a) Frequency modulation- The frequency of the carrier signal is altered in proportion to the message signal
- b) Amplitude modulation- The amplitude of the carrier signal is changed in proportion to the message signal while the phase and frequency are kept constant.
- c) Phase modulation- The phase of the carrier signal is altered
- Youtube video to watch- Lesics
The topic for the next class:- 5G and other topics in ICT.